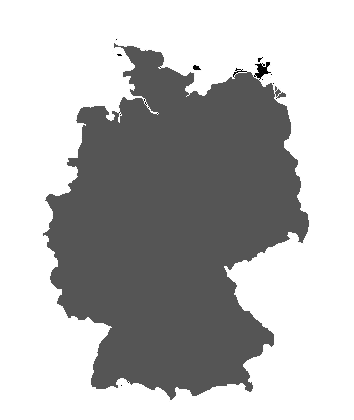
Deutschland

Germany |

Allemagne |

Alemania |

Germania |

ドイツ |
Federal republic
Bicameral Parliament or Parlament consists of the Federal Council or Bundesrat (69 seats; members appointed by each of the 16 state governments or landtags) and the Federal Diet or Bundestag (631 seats - total seats can vary each electoral term; approximately one-half of members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote and approximately one-half directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote; members serve 4-year terms)
Three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and gold; these colors have played an important role in German history and can be traced back to the medieval banner of the Holy Roman Emperor - a black eagle with red claws and beak on a gold field

|
"Das Lied der Deutschen"
(Song of the Germans) |
golden eagle
National colors: black, red, yellow |
President Joachim GAUCK (since 23 March 2012)
|
-
18 January 1871
(establishment of the German Empire)
divided into four zones of occupation
(UK, US, USSR, and France) in 1945 following World War II
Federal Republic of Germany
(FRG or West Germany) proclaimed on 23 May 1949 and included the former UK, US, and French zones
German Democratic Republic
(GDR or East Germany) proclaimed on 7 October 1949 and included the former USSR zone
West Germany and East Germany unified on 3 October 1990
all four powers formally relinquished rights on 15 March 1991
notable earlier dates: 10 August 843
(Eastern Francia established from the division of the Carolingian Empire)
2 February 962
(crowning of OTTO I, recognized as the first Holy Roman Emperor)
-
Unity Day, 3 October (1990)
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CD, CDB, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC |
Berlin
52 31 N, 13 24 E
UTC+1
BERLIN 3.563 million
Hamburg 1.831 million
Munich 1.438 million
Cologne 1.037 million
|
|
16 states (Laender, singular - Land)
Baden-Wuerttemberg, Bayern (Bavaria), Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen (Hesse), Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania), Niedersachsen (Lower Saxony), Nordrhein-Westfalen (North Rhine-Westphalia), Rheinland-Pfalz (Rhineland-Palatinate), Saarland, Sachsen (Saxony), Sachsen-Anhalt (Saxony-Anhalt), Schleswig-Holstein, Thueringen (Thuringia) |